National Maternity and Neonatal Safety Improvement Programme (MatNeoSIP)
This programme started in April 2017 and is aimed at supporting improvement in the quality and safety of maternity and neonatal units across England.
The overall aim of this National programme is to improve outcomes and reduce unwarranted variation by providing a safe, high quality healthcare experience for all women, babies and families across maternity and neonatal care settings.
The Regional MatNeoSIP Team works closely with:
- Northern Clinical Networks – Maternity
- Northern Neonatal Network
- Local Maternity System
- All Trusts in the region which have a maternity and neonatal unit
Phase 1
Phase 1 of this programme started in 2017 and very much focused on Trusts working on projects which would improve their own services. Some fantastic achievements were made by the end of Phase 1 (March 2021), with some, but by no means all, being outlined below.
- County Durham and Darlington NHS FT: Demonstrated a downward trend for admissions to the neonatal units for hypoglycaemic episodes, through the encouragement of bringing in colostrum (expressed milk prior to birth) into the acute hospital for delivery
- Gateshead Health NHS FT: More than 63% of Glucose Tolerance Tests (GTT) are now being performed correctly and they are seeking to continue to improve on this rate
- North Tees and Hartlepool NHS FT: 100% of women risk assessed for diabetes, hypertension, small gestational age, and venous thromboembolism at the booking appointment and evidenced in the hand held notes
- North Cumbria Integrated Care NHS FT: Over 80% of staff trained to undertake CO (carbon monoxide) monitoring and over 85% of women receiving CO screening at booking
- Northumbria Healthcare NHS FT: CO monitoring at booking reached 97% and CO monitoring at 36 weeks reached 77%
- The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS FT: 100% of maternity records show evidence of a MEWS (Maternity Early Warning Score) chart demonstrating the number of triggers and charts with appropriate review
- South Tees Hospitals NHS FT: Reduced the percentage of pregnant women smoking at delivery from 19% to 16.5%
- South Tyneside and Sunderland NHS FT: Over 80% of women have CO monitoring at booking
In addition:
- Nearly 2000 staff from maternity and neonatal units across the region completed culture surveys
- Staff from all eight Trusts were trained in improvement science by the IHI.
Phase 2
Phase 2, which started in April 2021, focuses on regional projects, building on the work from phase 1.
Current focus is particularly on the optimisation and stabilisation of the preterm infant which includes seven key interventions:
Place of birth: Extreme preterm birth in a tertiary unit setting significantly improves survival and neurodevelopmental outcomes
Antenatal steroids: The use of antenatal steroids significantly improves survival by reducing the risk of preterm lung disease, brain haemorrhage, necrotising enterocolitis (NEC) and sepsis
Magnesium sulphate: The use of magnesium sulphate within 24 hours prior to birth significantly reduces the risk of cerebral palsy
Intrapartum antibiotics: The use of antibiotics four hours before birth significantly improves survival outcomes by reducing the risk of Group B Streptococcus sepsis
Optimal cord management: Delayed cord clamping can significantly improve survival by reducing the risk of brain haemorrhage as well as the need for blood transfusion
Normothermia: Early hypothermia (< 36.5 degrees Celsius) increases the risk of mortality and brain haemorrhage, NEC and sepsis. Emerging evidence links early hypothermia (< 38 degrees Celsius) to adverse outcomes
Maternal breast milk: The safest milk for preterm babies is maternal breast milk as it significantly improves survival by reducing the risk of sepsis and NEC
Another one of our regional projects is looking at improving the number of smoke free pregnancies. A considerable amount of work is already ongoing throughout the region regarding this and therefore our focus has been on the introduction of Smoking Cessation Enhanced Support within those Trusts where this is not already in place.
Culture plays a key role in supporting change. We have therefore developed a document outlining some useful resources to support building positive cultures. This document can be viewed by clicking the link below.
Resources to support building positive cultures PDF
Further information
For further information please visit NHS England » The National Patient Safety Improvement Programmes
There are also two virtual hubs for this programme, one national and one regional. Please do join one or both to keep up to date with MatNeoSIP:
Regional Hub: MatNeoSIP Patient Safety Network for North East and North Cumbria – FutureNHS Collaboration Platform
National Hub: Maternity and Neonatal Safety Improvement Programme – FutureNHS Collaboration Platform
Evaluation of Episcissors-60
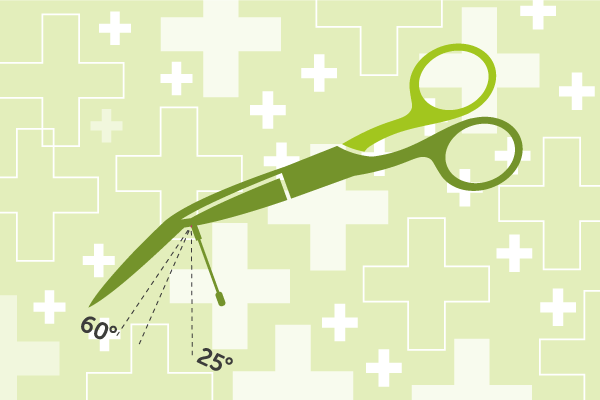
An Evaluation of Episcissors-60 Project lead: Dr. Paul Auyk (The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust) Perineal tears occur in 9 out of 10 women having a vaginal birth. In 1 in 20 women, the tear extends to involve…
Enhancing Experience in the Maternity Unit
Enhancement of the experience of women and families during maternity care using real time feedback and postal surveys and provision of targeted support to women experiencing traumatic birth using real time birth reflections Project lead: Ms Ruth James (South Tees…

